In today’s digital landscape, security audits have become indispensable for organizations to not only comply with stringent laws and regulations but also to fortify their defenses against increasingly sophisticated data breaches. The essence of data security lies in rigorous and regular assessments that evaluate how well an organization’s information is protected. Proactive security audits mitigate cyber risks and fortify an organization’s reputation by protecting sensitive data.

Delving into the key components of security audits, understanding their dynamics, discerning the frequency at which they should be conducted, and differentiating them from related practices such as penetration testing and vulnerability assessments involve a comprehensive approach. This knowledge is pivotal for organizations aiming to build a robust cybersecurity framework that effectively thwarts threats while ensuring continuous compliance. By drawing on expert insights and the latest strategies in the field, companies can navigate the complexities of data security with confidence and precision.
Understanding Security Audits
At the core of maintaining a robust defense against cyber threats, information security audits stand as pivotal evaluations designed to unearth vulnerabilities and detect any evidence of breaches. These assessments critically examine an organization’s systems to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information.
Types and Components of Security Audits:
- Internal vs. External Audits:
- Internal Audit: Conducted by organization members to self-assess security measures.
- External Audit: Performed by independent auditors, offering an unbiased review of security practices.
- Physical Security Audits:
- Essential in safeguarding property and individuals, focusing on:
- Access Control
- Surveillance
- Testing of security systems
- Essential in safeguarding property and individuals, focusing on:
Security audits meticulously evaluate an organization’s adherence to best practices, standards, and regulations. They cover a comprehensive scope, assessing:
- Physical components and environment
- Applications and software security
- Network vulnerabilities
- Human factors in data handling
- Overall security strategy
Security audits, through comparison with IT standards, guide remediation and risk assessment efforts, aid in developing strong mitigation strategies, safeguard sensitive data and ensure adherence to security policies and regulations.
Importance of Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are crucial in today’s dynamic digital environment, serving as a key defense by detecting system vulnerabilities that could be targeted by cybercriminals. Businesses doing frequent audits can identify and rectify weaknesses, thereby considerably lowering the risk of cyber attacks. Upholding data security integrity and adhering to industry regulations like HIPAA or PCI DSS necessitates such proactive measures.
- Key Benefits of Regular Security Audits:
- Vulnerability Identification: Uncover potential weaknesses in cybersecurity measures, including outdated software or inadequate password policies.
- Compliance Assurance: Ensure adherence to industry regulations, reducing legal and financial risks.
- Reputation and Trust: Protect the company’s reputation and maintain customer loyalty by preventing cyber attacks.
- Cost Savings: Mitigate financial losses associated with data breaches, with companies investing in regular audits having a 40% lower risk of experiencing such incidents.
- Strategic Risk Management: Provide a comprehensive overview of potential threats, allowing for the development of effective mitigation strategies.
Furthermore, conducting regular security audits plays a crucial role in maintaining a robust defense against evolving security threats. By continuously testing and training the security apparatus and personnel, organizations ensure that they are prepared to address current vulnerabilities and are also equipped to anticipate and counter future challenges. Engaging in this continuous improvement cycle is vital for safeguarding digital assets, upholding customer trust, and maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture in the face of ever-changing cyber threats.
Key Components of a Successful Security Audit
To ensure the efficacy of a security audit, several key components must be meticulously addressed:
- Review and Consolidation of Cybersecurity Policies and Approaches:
- Cybersecurity Policy Review: Auditors must evaluate the organization’s cybersecurity policies against both industry and global standards to ensure comprehensive coverage and compliance.
- Integrated Cybersecurity Framework: By centralizing cybersecurity, risk management, and compliance into a single document, auditors can gain a holistic view of the organization’s cybersecurity health.
- Personnel and Risk Management:
- Cybercompetence Evaluation: It’s crucial to assess the cyber literacy of all employees, including leadership, to ensure they are equipped to handle evolving cyber risks.
- Risk-Based Audit Strategy: Audit activities should prioritize areas of highest risk, focusing resources where they are needed most to mitigate potential threats effectively.
- Comprehensive Audit Execution:
- Audit Steps: From defining the audit scope and criteria to conducting risk assessments and technical testing, each step is vital for uncovering vulnerabilities and assessing compliance.
- Challenge Mitigation: Addressing common audit challenges such as unclear objectives, complex IT infrastructures, and evolving threats requires strategic planning, skilled resource allocation, and continuous improvement efforts.
This structured approach not only identifies weaknesses but also provides actionable insights for strengthening the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
How Often Should You Conduct Security Audits?
Determining the optimal frequency for conducting security audits is a multifaceted process, influenced by a variety of critical factors. These include:
- Organizational Factors:
- Size of the IT infrastructure
- Sensitivity of data
- Industry-specific compliance requirements
- Previous cybersecurity incidents
- Regulatory Compliance Frequencies:
- PCI Compliance: Every 90 days
- HIPAA Compliance: Triggered by specific factors, no set time
- NIST Compliance: Every two years
- Audit Types and Recommended Frequencies:
- Routine Audit: Twice a year
- Event-Based Audit: As needed, following significant network disruptions
For most organizations, a minimum of one comprehensive cybersecurity audit annually is advisable. However, entities handling sensitive information or subject to volatile threat landscapes should consider semi-annual audits. The decision on frequency should also account for operational changes, resource availability, and the introduction of new compliance standards. This tailored approach ensures that security audits remain a proactive and integral part of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy, adapting to its unique needs and the evolving digital threat landscape.
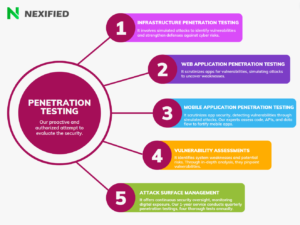
Comparing Security Audits, Penetration Testing, and Vulnerability Assessments
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding the nuanced differences between vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits is crucial for organizations aiming to fortify their defenses against cyber threats. Each of these methodologies plays a unique role in the overarching security strategy, yet they are often mistakenly used interchangeably.
- Vulnerability Assessment vs. Penetration Testing:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Utilizes automated tools to detect and categorize vulnerabilities within a system. It provides a broad overview of security weaknesses but does not delve into the exploitability or potential impact of these vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing (Pen Testing): Involves active exploitation of vulnerabilities to assess their severity and potential damage. This manual process builds upon the findings of vulnerability assessments to offer in-depth insights, including the detection of business logic errors and zero false positives, which automated assessments might overlook. Learn more about Pentesting.
- Integration with Security Audits:
- While both vulnerability assessments and penetration tests focus on identifying and exploiting system vulnerabilities, they are components of a comprehensive security audit. Security audits encompass a wider scope, evaluating an organization’s adherence to security policies, regulations, and best practices. They leverage the findings from vulnerability assessments and penetration tests to provide actionable recommendations for strengthening security measures.
The significance of utilizing a multi-faceted cybersecurity strategy, combining vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits to identify and fix potential threats is highlighted in this comparison.
Conclusion
Through this comprehensive exploration, we’ve underscored the criticality of regular security audits in today’s digitally-driven environment. These assessments are not merely regulatory check boxes but are foundational to identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance, and safeguarding sensitive data from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. The importance of implementing a robust cybersecurity framework, informed by expert insights and security best practices, cannot be overstated. It is through such diligence that organizations can maintain the integrity of their data, protect their reputation, and foster trust among their stakeholders.
Understanding the complexities involved in security audits, including their frequency, scope, and integration with other cybersecurity measures like penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, equips organizations to navigate digital risks more effectively. As a proactive step towards fortifying your cybersecurity posture, feel free to Contact Us for security audits. By doing so, you ensure that your organization is not only prepared but resilient against the challenges posed by cyber threats, positioning yourself for continued growth and success in a perpetually connected world.
FAQs
What is the significance of conducting regular security audits?
Regular security audits are essential for safeguarding critical data, pinpointing security weaknesses, formulating new security guidelines, and evaluating the success of existing security measures. They ensure that employees adhere to prescribed security protocols and are instrumental in identifying emerging vulnerabilities.
How do regular security audits and vulnerability assessments contribute to network security?
Regularly scheduled network security audits are vital for uncovering vulnerabilities within the network infrastructure, allowing for their proactive mitigation. These audits assess the robustness of firewalls, encryption methods, and access control mechanisms, thereby strengthening an organization’s defense against potential security threats.
How do security audits differ from vulnerability assessments?
Security audits are comprehensive evaluations encompassing all aspects of a security framework, whereas vulnerability assessments focus on identifying and addressing weaknesses in a specific area or component. Essentially, a vulnerability assessment is a component of a broader security audit.
What entails an information security audit for preventing information vulnerabilities?
An information security audit involves scrutinizing systems and operational procedures to unearth vulnerabilities that might result in a data breach or to uncover evidence of a breach that has already occurred. This process is critical for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of information.
Learn more about Vulnerabilities.