In today’s digital age, businesses of all sizes face the constant threat of cyberattacks. The consequences of a successful breach can be devastating, leading to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. It is no longer a question of “if” but “when” an organization will be targeted. To mitigate these risks, penetration testing services have emerged as a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. In this article, we will explore the importance of Pentesting and how it can help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems, networks, and applications.
Understanding Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, also known as Pentesting or Ethical hacking (Learn More🔗), is a security assessment process that involves simulating real-world cyberattacks to identify weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure. Unlike vulnerability assessments, which focus on identifying potential weaknesses, penetration testing goes a step further by actively attempting to exploit these vulnerabilities. By adopting the perspective of a malicious actor, skilled cybersecurity professionals perform controlled attacks to assess the resilience of an organization’s defenses.
The Purpose of Penetration Testing
The primary objective of Pentesting is to identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of existing security measures. By simulating real-world attacks, organizations can gain valuable insights into their current security posture and identify areas that require improvement. Penetration testing helps organizations:
- Identify Weaknesses: Pentesting exposes vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications, allowing organizations to understand the potential risks they face. By identifying weaknesses, organizations can take proactive measures to strengthen their defenses.
- Test Incident Response: Pentesting provides an opportunity to evaluate an organization’s incident response capabilities. By simulating an attack, organizations can assess their ability to detect, respond to, and recover from a security incident.
- Comply with Regulations: Many industries have specific compliance requirements that mandate regular Pentesting. Regulations such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require organizations to undergo Pentesting to ensure the security of sensitive data.
- Enhance Security Awareness: Pentesting raises awareness among employees about the potential risks of cyberattacks. It helps organizations foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness, ensuring that employees are vigilant and proactive in identifying and reporting potential threats.
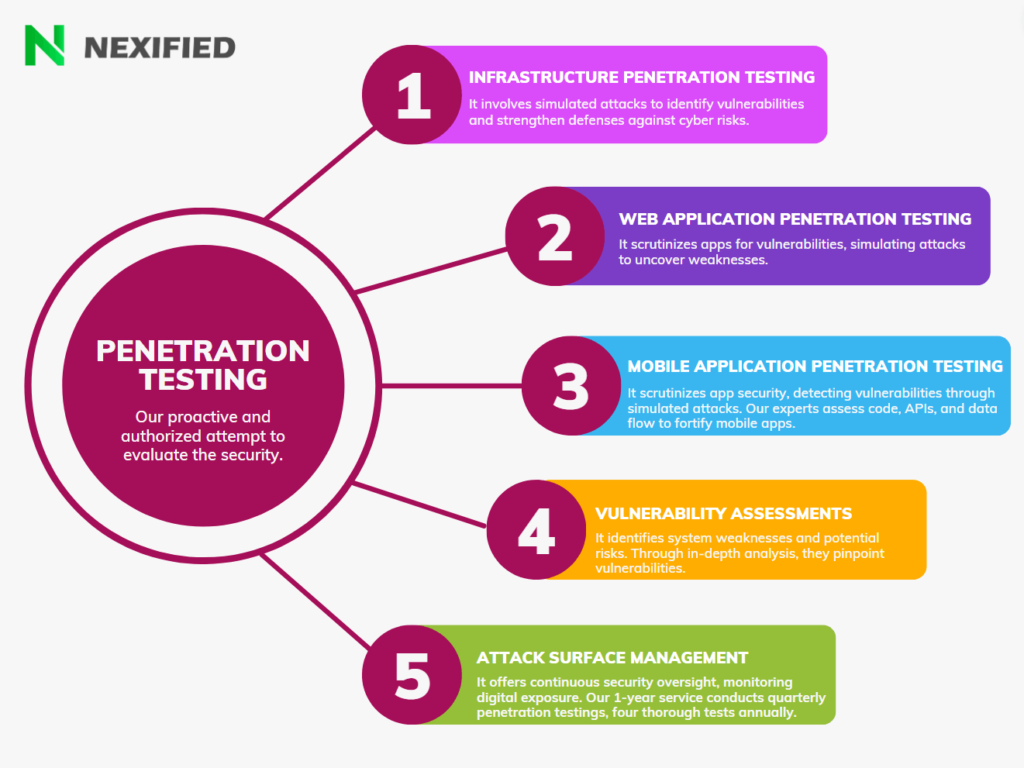
Types of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing can take various forms, depending on the scope and objectives of the assessment. Some common types of penetration testing include:
- Infrastructure Penetration Testing: This involves assessing the security of network infrastructure, including servers, firewalls, and other critical components. Our team employs advanced techniques to identify weaknesses and recommend robust security measures.
- Web Application Penetration Testing: With the increasing reliance on web applications, it’s essential to ensure that they are resilient against cyber threats. Our experts conduct thorough assessments of web applications to detect and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Mobile Application Penetration Testing: As mobile technology continues to proliferate, the security of mobile applications is paramount. We conduct in-depth evaluations of mobile apps to identify and address security gaps.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Our vulnerability assessments provide a comprehensive overview of an organization’s security posture, highlighting potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- Attack Surface Management: Understanding an organization’s attack surface is crucial for effective security management. Our services include identifying and managing the various points where an organization could be vulnerable to attack.
The Penetration Testing Process
The penetration testing process typically consists of the following steps:
- Planning and Scoping: The first step in a penetration test is to define the scope and objectives of the assessment. This involves identifying the systems, networks, and applications to be tested and determining the rules of engagement.
- Reconnaissance: During this phase, the penetration tester gathers information about the target organization. This may involve passive reconnaissance, such as collecting publicly available information, or active reconnaissance, such as scanning for open ports and services.
- Vulnerability Assessment: We conduct comprehensive vulnerability assessments that highlight potential weaknesses in an organization’s security posture, which attackers could exploit.
- Exploitation: The penetration tester identifies vulnerabilities and attempts to exploit them to gain unauthorized access or perform other malicious activities. This step involves using various techniques and tools to simulate real-world attacks.
- Post-Exploitation: After gaining access, the penetration tester evaluates the extent of the compromise and the potential impact on the organization. This phase helps organizations understand the severity of the vulnerabilities and prioritize remediation efforts.
- Reporting and Remediation: The final step involves documenting the findings and providing recommendations for remediation. We prepare a comprehensive report that details the discovered vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and provides actionable recommendations to address them.
The Importance of Penetration Testing
Penetration Testing plays a crucial role in maintaining robust cybersecurity defenses. Here are some key reasons why organizations should prioritize penetration testing:
Identifying Vulnerabilities
Penetration testing exposes vulnerabilities that may go undetected by automated scanning tools or manual inspections. By simulating real-world attacks, organizations can identify weaknesses in their systems, networks, and applications that could be exploited by malicious actors.
A penetration test allows companies to identify their vulnerabilities and understand how to exploit these weaknesses – whether it’s through revealing sensitive information, exposing the network, or applications.
Testing Incident Response
Penetration testing provides organizations with an opportunity to evaluate their incident response capabilities. By simulating an attack, organizations can assess their ability to detect, respond to, and recover from a security incident. This helps identify gaps in the incident response plan and allows for improvements to be made.
Penetration tests allow your company to evaluate the response of your IT team and their capabilities in the face of an attack, before an actual hacker targets your system. By identifying any gaps in their skill set during a simulated cyber attack, your cybersecurity team can then pursue additional training and further enhance their expertise.
Compliance Requirements
Many industries have specific compliance requirements that mandate regular penetration testing. Regulations such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require organizations to undergo penetration testing to ensure the security of sensitive data. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties and reputational damage.
Numerous sectors, including healthcare, banking, and service providers, incorporate penetration testing into their compliance regulations. Several well-known standards, such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, mandate the implementation of pen tests for compliance purposes.
Enhanced Security
Businesses, regardless of their size, are prime targets for cyberattacks. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable, with cyber criminals exploiting their limited resources and security measures. Penetration testing helps SMEs identify vulnerabilities and implement proactive security measures to safeguard their digital assets.
Small businesses are often targeted more heavily in cyberattacks. In the UK, around two-thirds of companies with 10 to 49 employees experienced cyber-crime incidents in the previous year.
Building Trust
Penetration testing demonstrates an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity and instills trust among stakeholders. Clients, partners, and customers feel reassured knowing that the organization takes its security seriously and actively seeks to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Incorporating penetration testing into your comprehensive cybersecurity strategy helps to establish trust with stakeholders, as it demonstrates a serious commitment to the company’s cyber defense.
Cost Savings
Investing in penetration testing can result in significant cost savings in the long run. By identifying vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate security measures, organizations can mitigate the risk of a successful cyberattack. The financial, reputational, and legal consequences of a breach far outweigh the cost of regular penetration testing.
By conducting penetration tests, businesses can enhance their security and minimize vulnerabilities by identifying and addressing weak areas. Investing in cybersecurity to proactively prevent such attacks can ultimately save businesses from the high costs associated with re-securing systems and networks.
Conclusion
In an increasingly interconnected and digitized world, the importance of penetration testing cannot be overstated. It serves as a proactive measure to identify vulnerabilities, test incident response capabilities, comply with regulations, enhance security, build trust, and ultimately safeguard an organization’s digital assets. By regularly conducting penetration tests and addressing identified vulnerabilities, organizations can fortify their cybersecurity defenses and stay ahead of potential threats. In today’s threat landscape, proactive action is essential to ensure the resilience and continuity of business operations. Invest in penetration testing services today to protect your organization from the ever-evolving cyber threats.